Decreasing our vascular age can affect our health age. If you would like to decrease your vascular age to promote overall health and longevity, consider Vascuclear.
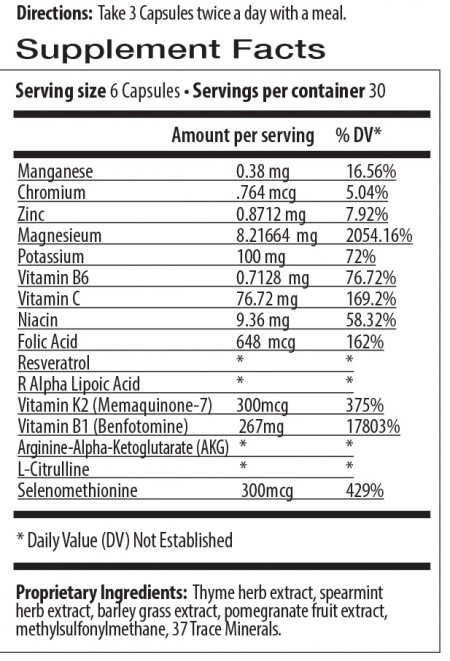
Our unique formulation of electrolytes with enzymes, amino acids, and vitamins.* It helps to support the body for better, healthier arterial function and a normal, healthy circulation of blood flow through the tiniest capillaries to your eyes, heart and kidneys.* Vascuclear supports vascular and muscular flexibility including blood vessels, arteries, and a healthy blood circulation.*
Vascuclear is an all-natural nutritional supplement may help the body support artery health and keep arteries healthy.
Vascuclear helps to support the health of the coronary arteries, which is a key factor in heart health. It important to be proactive and try to help keep your arteries strong and flexible to support long-term heart health.*
Vascuclear cutting-edge formulation may:
- Help support the health of the arteries*
- Improved vascular elasticity & maintain flexible arteries*
- Improves heart & vascular health*
- Promote healthy blood flow & circulation*
- Support overall body circulation*
- Prevent cardiovascular aging*
- Improve bone strength and mass*
- Maintain bone density by facilitating calcium transport into bone*
- Support healthy prostate*
- Support muscular flexibility*
- Increase Alkalinity pH*
- Free radical scavenger with powerful antioxidant properties*
- Helps reduce oxidative stress*
- Maintaining healthy homocysteine levels for heart health. Or Help maintain flexible arteries*
- Supports healthy homocysteine metabolism*
- Supports nerve, muscle, and brain health*
Vascuclear ingredients include:
K2 (MK-7): As we get older, it is important that our arteries remain elastic and flexible to carry blood and nutrients to all your cells and tissues. Much of that comes from the balance of vitamins K2, D, and calcium in the body.
Calcium should be moved to your bones and teeth, and not your arteries and organs. K2 plays a role in calcium uptake in bone. According to researchers, healthy arterial tissues contain up to 100 times more vitamin K2 than unhealthy arteries.*
Research has shown that low vitamin K inhibits the function of a protein called matrix Gla-protein (MGP). This protein is vitamin K dependent and must be carboxylated to function properly.1
When there is insufficient vitamin K, MGP remains uncarboxylated. Studies have found that uncarboxylated MGP builds up in the arteries.2,3 Without normal levels of carboxylated MGP, the integrity of the arteries is negatively impacted.4,5
The Rotterdam Heart Study, 4,800 patients for seven years were studied, and it showed that those who consume the most dietary K2 have healthier hearts then those who consume the least.6 A new study on vitamin K2 presented at the 13th International Nutrition and Diagnostics Conference (INDC 2013) in the Czech Republic supports vitamin K2’s role in heart health.9
“Our food is increasingly deficient in vitamin K2 in particular, and up to 98% of the general healthy population may be vitamin K2 insufficient with long-term detrimental impact on bone and cardiovascular health."
Approximately 97 percent of the Western hemisphere may be deficient in vitamin K2. It can be challenging to acquire enough K2 through our diet. By returning blood levels of vitamin K2 may help reverse vitamin K2 deficiency.*
Vascuclear’s unique formulation supplies a nutritional dose of 300 mcg of Vitamin K2 as natural MK-7 (menaquinone-7) in a bioactive, bioavailable form.
|
Alpha-lipoic acid is an antioxidant to support liver and nerve health, and protects against oxidation. Alpha-lipoic acid increases glutathione levels in cells already within a normal range and has antioxidant properites.1-3 Cellular oxidative damage is caused by free radicals. What Alpha-lipoic acid ability to extinguish free radicals on a cellular level. It also may chelate metals, to support the body purge itself of accumulated ingested toxins.4-7
Alpha-lipoic acid is a cofactor for some enzymes (alpha keto acid dehydrogenases) that produce energy from food and oxygen in mitochondria8-10 and thus plays a critical role in energy production within the cell’s mitochondria.
Alpha-lipoic reinforces essential antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, coenzyme Q10, and glutathione, and the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). The evidence is especially strong for the ability of DHLA (dihydrolipoic acid, a reduced form of alpha-lipoic acid) to recycle vitamin E. This is apparently achieved directly by quenching tocopherol radicals or indirectly by reducing vitamin C or increasing the levels of ubiquinol (a derivative of CoQ10) and glutathione, that, in turn, helps regenerate tissue levels of vitamin E. 8,11-17
Clinical studies have not reported serious adverse side effects, even at high doses. |
|
Resveratrol is a plant compound, found in red grapes. Resveratrol may be the most effective compound for maintaining optimal health and promoting longevity that may slow down the aging process and health overall.
In high doses, Resveratrol encourages healthy insulin sensitivity, mitochondrial function, and protects against the effects of a high-fat diet.2-16
Studies have shown, just as a calorie-restriction diet can set in motion active gene expression, which could slow down aging. The good news, resveratrol sparks many of the same favorable gene expression changes as calorie restriction, without dieting.*
In higher doses, resveratrol may promote healthy insulin sensitivity and encourages enhanced mitochondrial function,.*
|
References
Osteoporos Int. 2013 Sep;24(9):2499-507.
Atherosclerosis. 2012 Dec;225(2):397-402.
Adv Nutr. 2012 Mar 1;3(2):166-73.
Thromb Haemost. 2008 Oct;100(4):593-603.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Sep;3(5):1504-10.
J Nutr. 2004 Nov;134(11):3100-5.
Blood. 2007 Apr 1;109(7):2823-31.
J Vasc Res. 2003 Nov-Dec;40(6):531-7.2
NattoPharma 2013
Modern Rheumatology 2012 Nov 6. [Epub ahead of print]
Science 2012 Jun 8;336(6086):1306-10.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis September 2009
J Appl Physiol. 1999 Apr;86(4):1191-6.
Chem Biol Interact. 2006 Nov 7;163(3):192-8
Nutrition. 2007 Jan;23(1):76-80.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):C1395-403.
Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Jan;113(1):154-64.
Toxicol Lett. 2005 Dec 30;160(1):1-7.
Chem Biol Interact. 2004 Apr 15;147(3):259-71.
Chem Biol Interact. 2001 Nov 28;138(2):189-98.
Neurochem Res. 2007 Sep;32(9):1552-8
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Apr;959:491-507.
Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;22(1-2):359-78.
Free Radic Biol Med. 2001 Jul 1;31(1):53-61.
Z Naturforsch [C]. 1998 Mar-Apr;53(3-4):250-3.
Nutrition. 2001 Oct;17(10):888-95.
Gen Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;29(3):315-31.
Biochim Biophys Acta 1988 Dec 16;963(3):558-61
Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990 Jun 29;169(3):851-7.
Clin Interv Aging. 2008;3(2):331-9.
Cell Metab. 2011 Nov 2;14(5):612-22.
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012 Dec;67(12):1307-12.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Aug;55(8):1197-206.
Atherosclerosis. 2007 Apr;191(2):265-71.
Mol Cancer. 2006 Oct 17;5:45.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007 Jun;16(6):1246-52.
Prostate. 2009 Nov 1;69(15):1668-82.
Surgery. 2010 Aug;148(2):453-62.
Arch Med Res. 2010 May;41(4):288-94.
Dose Response. 2010 Mar 18;8(4):478-500.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2011 Dec;49(12):3319-27.
J Endocrinol Invest. 2011 Nov;34(10):788-92.
Neurosci Lett. 2011 Oct 10;503(3):250-5.
Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2011 Jul;39(3):128-32.
Nature. 2004 Aug 5;430(7000):686-9.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.